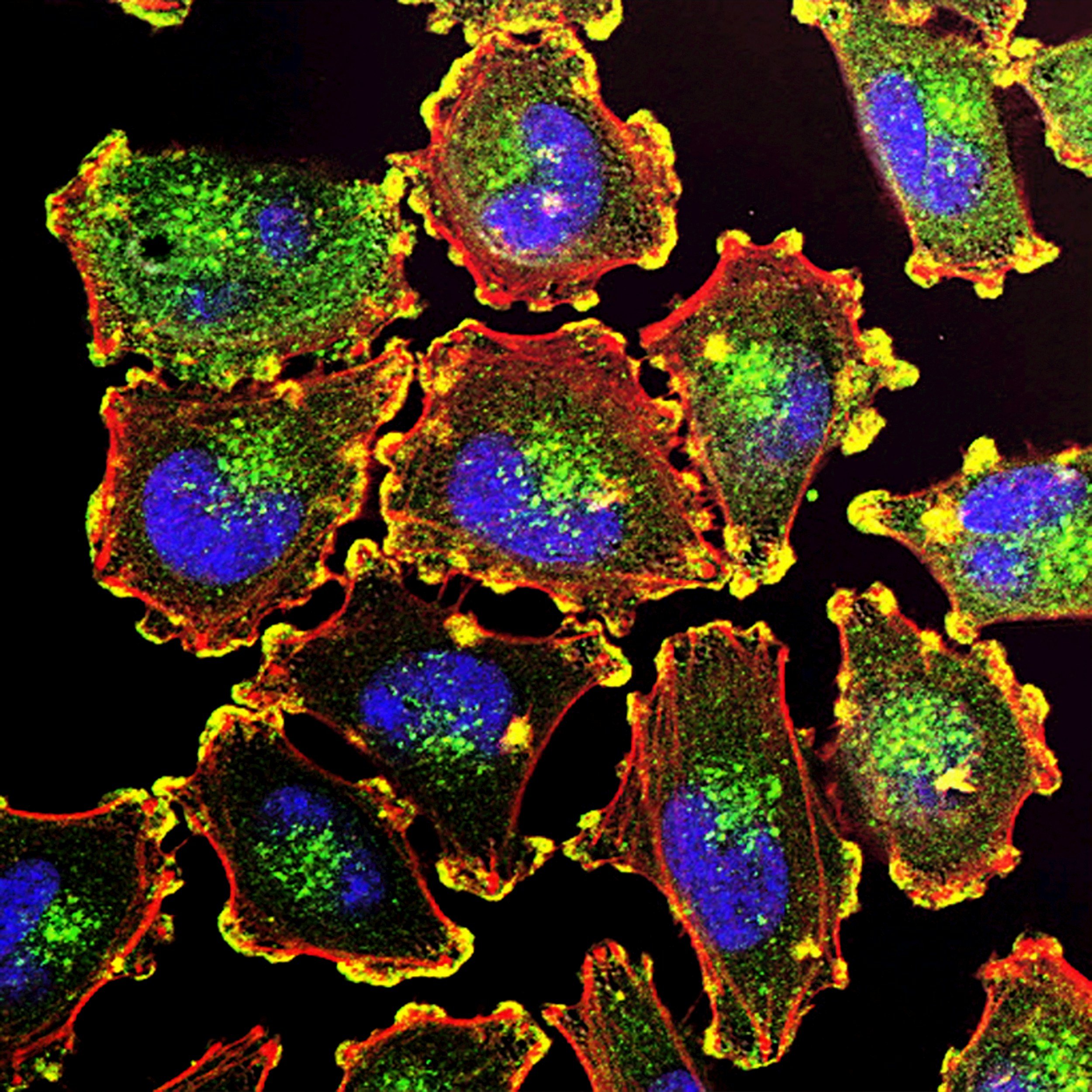
Luka’s mutation causes a single change in an amino acid, which reduces the function of the ATP6AP2 protein. This protein plays a key role in assembling the V-ATPase complex, also known as the Proton Pump, which helps regulate cellular balance.
This mutation is part of a broader group of V-ATPase defects, which have been linked to lysosomal storage disorders, congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG), and neurological conditions.